Solved overall reaction: 2NO(g)+O2(g)→2NO2(g) Step
4.8 (76) · € 20.99 · Auf Lager

![2NO(g)+O2(g)→2NO2(g) r=K[NO]2[O2](https://classroom-images.cdn.askfilo.com/classroom/1669396270162_rorvaapl_3232551.jpg)
2NO(g)+O2(g)→2NO2(g) r=K[NO]2[O2

Solved) - The Reaction 2NO2 ? 2NO + O2 Obeys The Rate Law: Rate = 1.4 X (1 Answer)

Solved Question 17 The following two-step mechanism has been

Reaction Kinetics
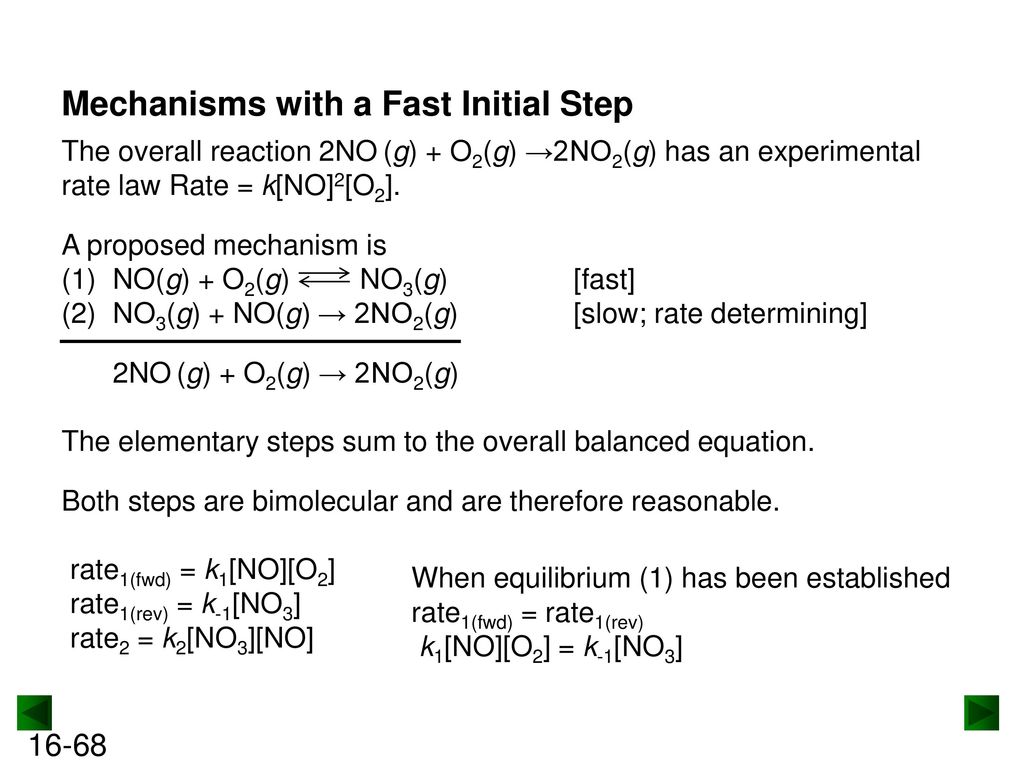
Chapter 16 Kinetics: Rates and Mechanisms of Chemical Reactions. - ppt download
![For a reaction, 2NO(g) + O2(g)→ 2NO2(g) Rate = k [ NO ]^2 [ O2 ] if the volume of the reaction vessel is doubled, then the rate of the reaction](https://dwes9vv9u0550.cloudfront.net/images/10009905/bfdb4986-049c-4251-98a7-35130ff48aba.jpg)
For a reaction, 2NO(g) + O2(g)→ 2NO2(g) Rate = k [ NO ]^2 [ O2 ] if the volume of the reaction vessel is doubled, then the rate of the reaction

The reaction 2NO(g) + O2(g) to 2NO2(g) exhibits the rate law, Rate = k(NO)2( O2). Which of the following mechanisms is consistent with this rate law?

Answered: 4.) The overall reaction 2NO2(g) +…

Consider this reaction : 2NO(2)(g)+O(3)(g)rarrN(2)O(5)(g)+O(2)(g)

SOLVED: The following two-step mechanism has been proposed: Overall reaction: 2NO(g) + O2(g) -> 2NO2(g) Step 1: NO + O2 -> NO3 Step 2: NO3 + NO -> 2NO2 slow fast What
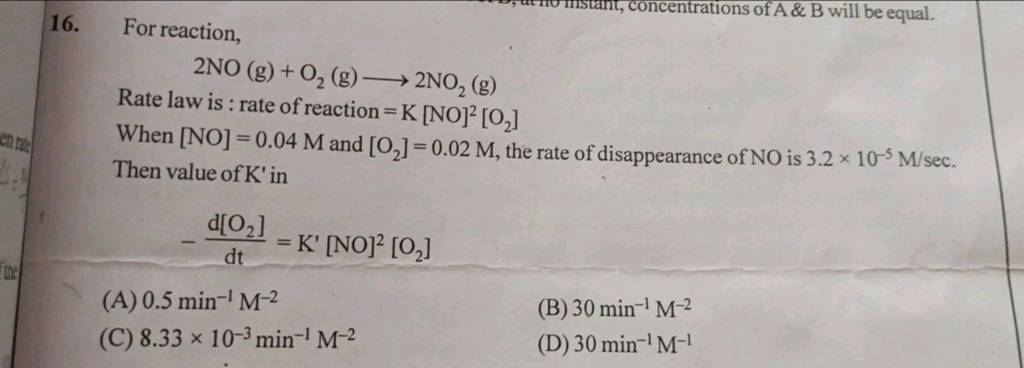
29 For reaction, 2NO(g)+O2( g)⟶2NO2( g) Rate law is : rate of reaction ..

For the reaction 2NO(g)+O2( g)→2NO2( g) calculate ΔG at 700 K when enth..

4. The dissociation of NO2 occurs by the following reaction: 2NO2(g) → 2NO(g) + O2(g) If the rate for the